-
Cybersecurity Governance Structure
+ Cybersecurity Governance Structure
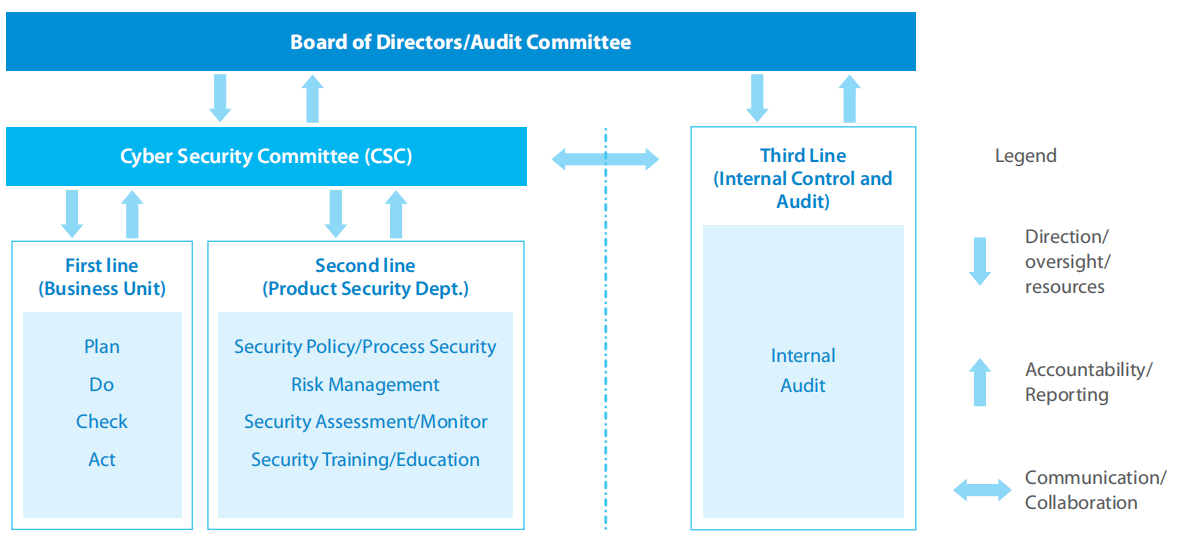
ZTE has a comprehensive cybersecurity governance structure to mitigate risk. ZTE's Cybersecurity Committee, chaired by the CEO, is the top decision-making organization, and ensures that industry-recognized cybersecurity practices are deployed and integrated across all business units. The first line are business units that implement self-control over the cybersecurity of products; the second line is the Product Security Department, implementing independent security assessment and supervision of first line security work; the third line is ZTE Internal Control & Audit, whose role is to audit the effectiveness of the first-line and second-line work.
-
Security Embedded Product Life Cycle
+ Security Embedded Product Life Cycle
ZTE uses industry standards and best practices to implement top-down, risk-based cybersecurity governance throughout the product life cycle. For supply chain, ZTE emphasizes the security and credibility of suppliers and guarantees continuity and resilience of supply. For R&D, ZTE embeds security controls in all stages of the R&D process, ensuring that products are secure by design and by default. For delivery, ZTE continues to benchmark the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) for security governance and has formed an end-to-end professional team to achieve efficient operations and secure network.
ZTE benchmarks the GSMA Network Equipment Security Assurance Scheme (NESAS) in its product development and lifecycle process and adopts the Building Security in Maturity Model (BSIMM) and Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) to formulate ZTE’s product security maturity model and corresponding specifications which are regularly assessed and improved.
-
Digital Infrastructure Supporting Product Life Cycle
+ Digital Infrastructure Supporting Product Life Cycle
ZTE has integrated security governance into the product lifecycle processes, and established the digital infrastructure for cybersecurity that runs through the front-line business units.
ZTE's digital systems, such as the Intelligent Supply Coordination Platform (ISCP), Product R&D Cloud (RD Cloud), and Global Customer Support Center (GCSC), achieve efficient operation in resilient supply, continuous planning, collaborative development, integrated testing, release and deployment, and problem solving. The configuration management system and vulnerability management system are used to efficiently track and trace security issues of products.
In addition, the DevSecOps tool chain is equipped to implement security management and controls in each phase. In key security activities such as material security testing, third-party software security scanning, code scanning, vulnerability scanning, version protection, and security hardening, security tools are used to automatically check whether products and services meet security requirements.